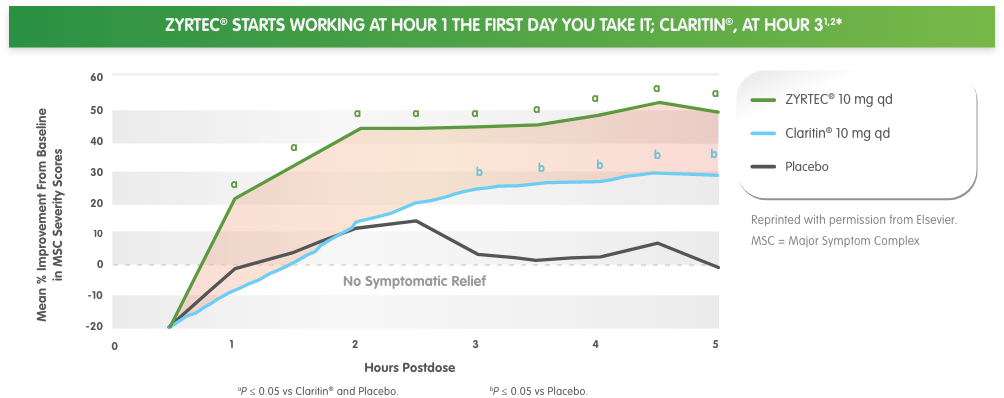
*ZYRTEC® 10 mg starts working at hour 1 and Claritin® starts working at hour 3, based on first dose on the first day of a 2-day study in 2 pollen- chamber studies. Primary endpoint measured mean improvement from baseline in Major Symptom Complex (MSC) severity score. MSC symptoms included runny nose, sniffles, itchy nose, nose blows, sneezes, and watery eyes.
†The environmental exposure unit (EEU) is an indoor chamber used to expose large groups of subjects to controlled levels of pollen comparable to those experienced outdoors during peak allergy season, and can be replicated regardless of time of year. The EEU is a validated, standard method of determining onset of action and duration of anti-allergic treatments.
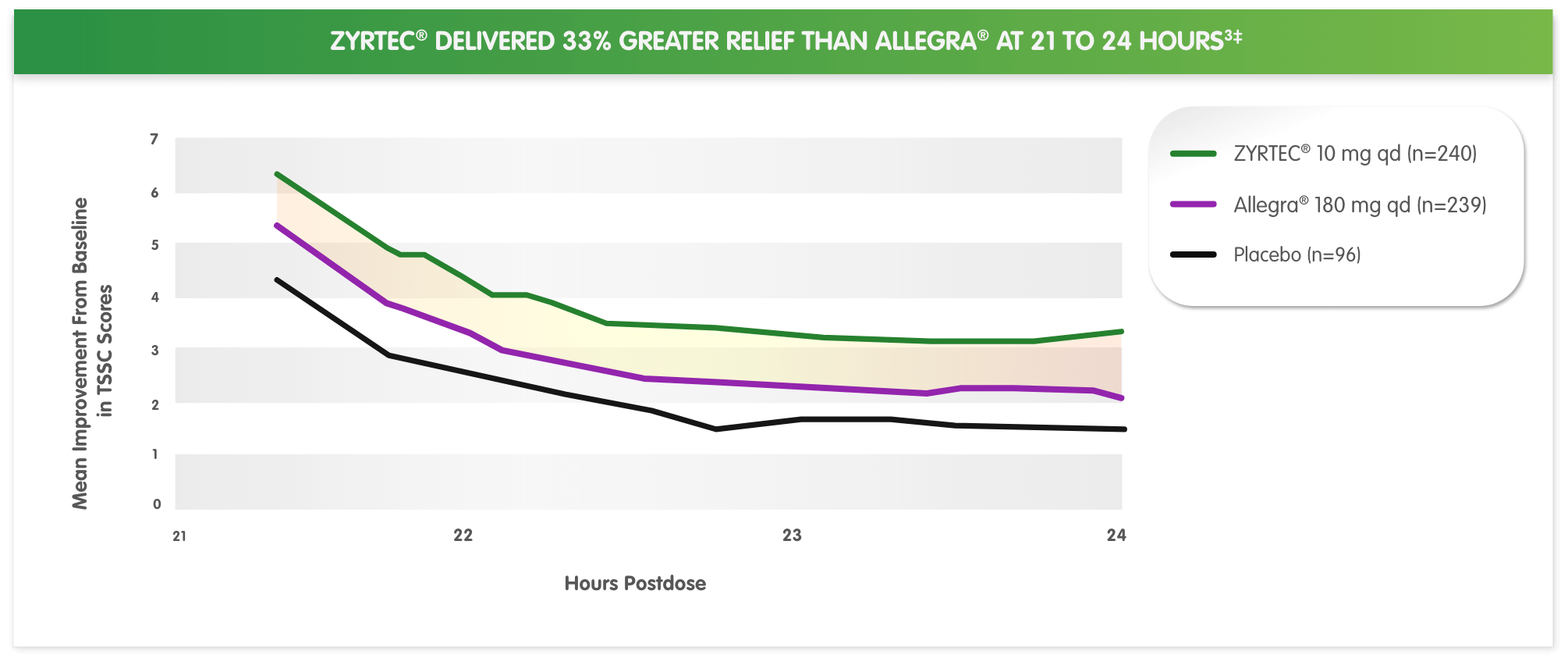
‡Based on first dose on the first day of a 2-day pollen-chamber study with ZYRTEC® 10 mg vs Allegra® 180 mg at hours 21 to 24. Primary efficacy endpoint was change in total symptom severity score from baseline at hours 21 to 24. Total symptom severity complex score was defined as the sum of self-assessed severity scores of 4 symptoms: runny nose, sneezing, itchy nose/palate/throat, and itchy/watery eyes.
References:
1. Day JH, Briscoe M, Widlitz MD. Cetirizine, loratadine, or placebo in subjects with seasonal allergic rhinitis: effects after controlled ragweed pollen challenge in an environmental exposure unit. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1998;101(5):638-645.
2. Day JH, Briscoe M, Rafeiro E, Chapman D, Kramer B. Comparative onset of action and symptom relief with cetirizine, loratadine, or placebo in an environmental exposure unit in subjects with seasonal allergic rhinitis: confirmation of a test system. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2001;87(6):474-481.
3. Day JH, Briscoe MP, Rafiero E, Hewlett D, Chapman D, Kramer B. Randomized double-blind comparison of cetirizine and fexofenadine after pollen challenge in the environmental exposure unit: duration of effect in subjects with seasonal allergic rhinitis. Allergy Asthma Proc. 2004;25(1):59-68.
4. Data on file. Johnson & Johnson Consumer Inc., McNeil Consumer Health Division.